Given the head of a linked list, reverse the nodes of the list k at a time, and return the modified list.
k is a positive integer and is less than or equal to the length of the linked list. If the number of nodes is not a multiple of k then left-out nodes, in the end, should remain as it is.
You may not alter the values in the list’s nodes, only nodes themselves may be changed.
Example 1:
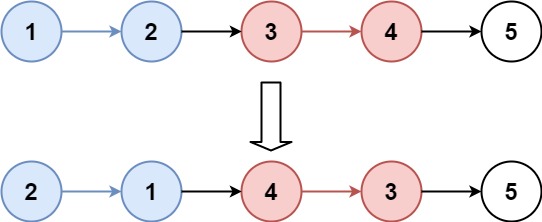
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 Output: [2,1,4,3,5]
Example 2:
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3 Output: [3,2,1,4,5]
C++ Solution
struct ListNode {
int val;
ListNode *next;
ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
void reverse(ListNode s,ListNodee){
ListNode *p=NULL,*m=s, *n=s->next;
while(p!=e){
m->next = p;
p=m;
m=n;
if(n!=NULL)
n= n->next;
}
}
ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k)
{
if(head == NULL || k==1|| head->next == NULL)
{
return head;
}
ListNode* dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy->next=head;
ListNode *bf = dummy,*e=head;
int count=k-1,i=0;
// ListNode *s=head,*e=head;
while(e!=NULL)
{
i++;
if(i%k==0){
ListNode *s= bf->next,*temp=e->next;
reverse(s,e);
bf->next=e;
s->next = temp;
bf=s;
e=temp;
}
else{
e=e->next;
}
}
return dummy->next;
}
};Java Solution :
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
int n = 0;
ListNode temp = head;
while(temp!=null){
n++;
temp = temp.next;
}
int times = n / k;
temp = null;
ListNode current = head, prev = null, nextL, start;
for(int i = 0; i< times; i++){
start = current;
// prev = current;
// current = temp;
for(int j = 0; j<k ; j++){
nextL = current.next;
current.next = prev;
prev = current;
current = nextL;
}
// temp = current;
start.next = current;
if(temp == null){
head = prev;
temp = start;
}
else{
temp.next = prev;
temp = start;
}
prev = start;
}
// prev.next = null;
return head;
}
}Python Solution :
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverse(self,head):
prev=None
pres=head
fut=head.next
while pres:
pres.next=prev
prev=pres
pres=fut
if fut:
fut=fut.next
return prev,head
def reverseKGroup(self, head: Optional[ListNode], k: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
ptr=head
fir=None
while ptr:
val=k
sec=ptr
while val>1:
sec=sec.next
if not sec:
return head
val-=1
temp=sec.next
sec.next=None
h,t=self.reverse(ptr)
if fir:
fir.next=h
else:
head=h
t.next=temp
fir=t
ptr=temp
return head