LeetCode .905 Sort Array By Parity : Hey there, coding enthusiasts! Welcome back to another exciting coding session. Today’s problem is a treat—literally! We’re going to solve the “ Sort Array By Parity” or “LeetCode .905”
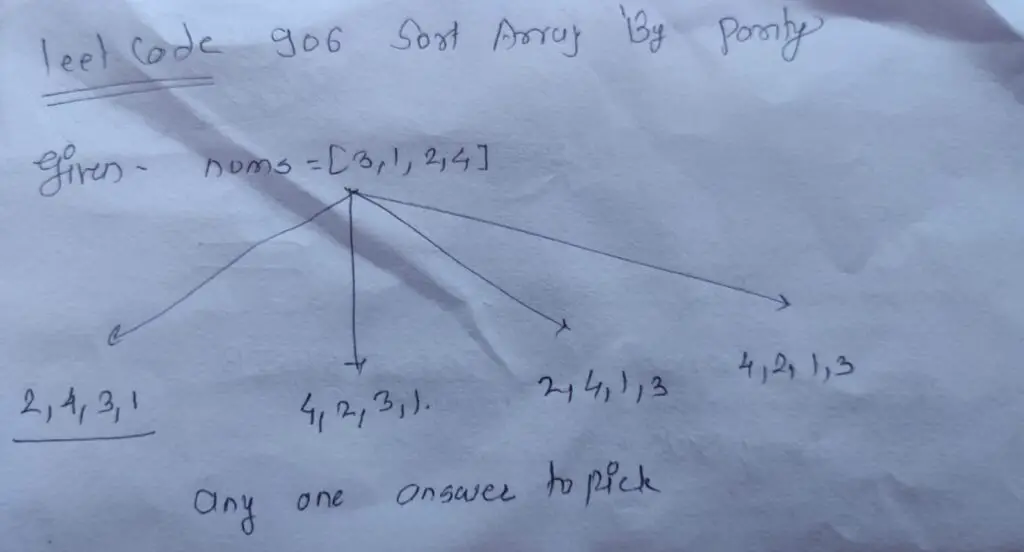
1 Approach : Two vector (Array) : Leet Code 950

Step for Two array approach
1: Initialize Lists
- Begin by creating three empty array ,lists:
ans,odd, andeven.
2: Iterate Through Array
- Loop through the given array from “Leetcode 905,” examining each number.
3: Separate Even and Odd Numbers
- For each number, check if it’s even or odd based on its remainder when divided by 2.
- If it’s even, add it to the
evenlist; otherwise, add it to theoddlist.
4: Combine Lists
- After processing all numbers, concatenate the
evenandoddlists in that order. This combines the numbers while preserving their respective orders.
Step 5: Return Sorted Array
- The
anslist now holds the sorted array with even numbers appearing before odd numbers. - Return this sorted array as the result of the function.
C++: Sort Array By Parity (Two Array Approach)
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> sortArrayByParity(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int> ans;
vector<int> odd;
vector<int> even;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if(nums[i] % 2 == 0) {
even.push_back(nums[i]);
} else {
odd.push_back(nums[i]);
}
}
ans = even;
for(int i = 0; i < odd.size(); i++) {
ans.push_back(odd[i]);
}
return ans;
}
};Java: Sort Array By Parity (Two Array Approach)
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
class Solution {
public List<Integer> sortArrayByParity(int[] nums) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> odd = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> even = new ArrayList<>();
for (int num : nums) {
if (num % 2 == 0) {
even.add(num);
} else {
odd.add(num);
}
}
ans.addAll(even);
ans.addAll(odd);
return ans;
}
}Python: Sort Array By Parity (Two Array Approach)
class Solution:
def sortArrayByParity(self, nums):
ans = []
odd = []
even = []
for num in nums:
if num % 2 == 0:
even.append(num)
else:
odd.append(num)
ans.extend(even)
ans.extend(odd)
return ansJavaScript: Sort Array By Parity (Two Array Approach)
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number[]}
*/
var sortArrayByParity = function(nums) {
let ans = [];
let odd = [];
let even = [];
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] % 2 === 0) {
even.push(nums[i]);
} else {
odd.push(nums[i]);
}
}
ans = even.concat(odd);
return ans;
};

2 Approach 1: Two-Pointer Approach
To solve the “Sort Array By Parity” problem using the two-pointer approach:
Key Data Structures:
- i and j: Two pointers initialized to the start and end of the array, respectively.
Enhanced Breakdown:
- Initialization:
- Initialize
ito 0 andjto the last index of the array.
- Initialize
- While Loop:
- Keep iterating until
iis less thanj. - Increment
iif the element atiis even. - Decrement
jif the element atjis odd. - Swap the elements at
iandjif the above conditions aren’t met.
- Keep iterating until
- Return the Modified Array:
- After the loop completes, the array will be sorted by parity.
Codes for Leet code 905 Two Pointer Approach
C++: Leet code 905
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> sortArrayByParity(vector<int>& nums) {
int i = 0, j = nums.size() - 1;
while (i < j) {
while (i < j && nums[i] % 2 == 0) {
i++;
}
while (i < j && nums[j] % 2 == 1) {
j--;
}
swap(nums[i], nums[j]);
}
return nums;
}
};Java: Leet code 905
class Solution {
public int[] sortArrayByParity(int[] nums) {
int i = 0, j = nums.length - 1;
while (i < j) {
while (i < j && nums[i] % 2 == 0) {
i++;
}
while (i < j && nums[j] % 2 == 1) {
j--;
}
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
return nums;
}
}Python : Leet code 905
class Solution:
def sortArrayByParity(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[int]:
i, j = 0, len(nums) - 1
while i < j:
while i < j and nums[i] % 2 == 0:
i += 1
while i < j and nums[j] % 2 == 1:
j -= 1
nums[i], nums[j] = nums[j], nums[i]
return numsLeet Code 1658. Minimum Operations to Reduce X to Zero (Medium)
JavaScript: Leet code 905
function sortArrayByParity(nums) {
let i = 0, j = nums.length - 1;
while (i < j) {
while (i < j && nums[i] % 2 === 0) {
i++;
}
while (i < j && nums[j] % 2 === 1) {
j--;
}
[nums[i], nums[j]] = [nums[j], nums[i]];
}
return nums;
}Result Analysis :
List Of Some Important leetcode Question :